OpenTimestamps is a standard format for blockchain timestamping.
The reference implementation is written in Python by Peter Todd, and there are libraries in different languages: javascript, java, rust.
Opentimestamps javascript library is written for nodejs and npm package is publicly available. OpenTimestamps library could be used also on the client side, for more details check browser compatibility.
Now let’s begin!
- Get started with opentimestamps.js
- Get the hash of a file
- Timestamp hash and retrieve the proof
- Get information about the proof
- Upgrade a pending proof
- Verify the ots proof on the blockchain
JS OpenTimestamps web-interface and web-tools are available at opentimestamps.org/tools
Get started with opentimestamps.js
In order to get the opentimestamps.js you can proceed in the following manner:
Download a ready file from the website opentimestamps.org (or directly include in your page)
<script src="https://opentimestamps.org/assets/javascripts/vendor/opentimestamps.js"></script>
Or build sources from javascript-opentimestamps
git clone https://github.com/opentimestamps/javascript-opentimestamps.git
npm install --dev
npm run dist
and add to html page:
<script src="./dist/opentimestamps.js"></script>
Get the hash of a file
The first step in order to create a timestamp of a file calculates the hash of the file, you can calculate this hash directly from the webpage using Javascript in the following manners:
- using the library crypto-js from string object
<script type="text/javascript" src="/crypto-js.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var encrypted = CryptoJS.SHA256("...")
</script>
- using hash function available in javascript-opentimestamps from byte array
<script type="text/javascript" src="/opentimestamps.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
const op = new OpenTimestamps.Ops.OpSHA256()
const hashByteArray = op.call([...])
</script>
OpenTimestamps supports only sha1, sha256 and ripemd160 hash functions.
Timestamp hash and retrieve the proof
After the calculation of the hash (in hexadecimal format) you can call the methods to generate the timestamps like show in the following code :
const hashData = "16193782f1d839a08f9fc9a94cec1675f1729db1abc15cf9b57f31aa1724a0ae"
const op = new OpenTimestamps.Ops.OpSHA256()
const detached = OpenTimestamps.DetachedTimestampFile.fromHash(op, hashData)
OpenTimestamps.stamp(detached).then( ()=>{
const ots = detached.serializeToBytes()
const hex = bytesToHex(ots)
console.log(hex)
})
The first step is to create an OpenTimestamps.DetachedTimestampFile object which is the virtual representation of a proof in OpenTimestamps protocol. The proof is a merkle tree of data where the original hash is the head and attestations are the tips.
To create a new detached object use fromHash() constructor and pass as input parameters:
- hash type instance of
OpenTimestamps.Ops(supported:OpSha1,OpSha256,OpRimepd160) - hash data in hex format
Use
fromBytes()constructor to create a new detached file from an array of bytes, insteadfromHash()
Then call OpenTimestamps.stamp() to timestamp the hash inside detached object.
In
stamp()function,detachedis an input / output parameters, sinceOpenTimestamps.DetachedTimestampFileis the proof.
A detached proof could be serialized to bytes with serializeToBytes() and download as ots file; vice-versa, deserialize an byte array to an object with OpenTimestamps.DetachedTimestampFile.deserialize(ots).
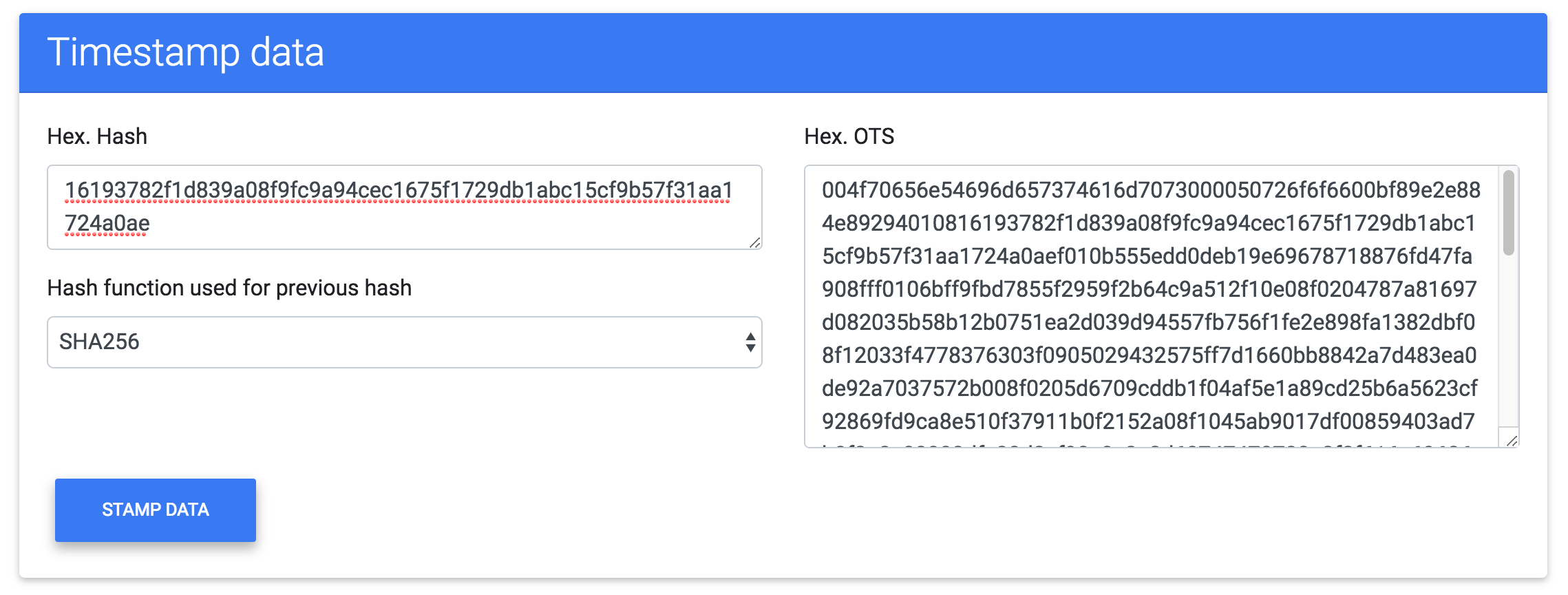
Get information about the proof
The stamp command instantly provides an OpenTimestamps proof which contains the promised attestation of the stamped hash.
You can use the info command in order to visualize the binary ots in a human-readable format.
const detached = OpenTimestamps.DetachedTimestampFile.deserialize(ots)
const output = OpenTimestamps.info(detached)
console.log(output)
The info output is a chain of crypto-operation that describe a path from the originally stamped hash to one or more attestations. The info of the previous example shows:
File sha256 hash: 16193782f1d839a08f9fc9a94cec1675f1729db1abc15cf9b57f31aa1724a0ae
Timestamp:
append c04158b183a378f3d051d55979a918d8
sha256
-> append 89c144ad44156173d93cd470569c3087
sha256
prepend d37278872acc324f499d54dd488fbe29f76d892204793701e38129e0a2f224b0
sha256
prepend 333ea54d67017894b5e581b2bd4e197d3990c031bc78331b7e5c9ee89162c8fd
sha256
append bdef644af9388e148d198dec47e62fdaf9e264baf28f9e8115f0468354b2cc44
sha256
prepend 5ab7a0c9
append 05765ac5abc32c3b
verify PendingAttestation('https://alice.btc.calendar.opentimestamps.org')
-> append 26ef6425656e1095c5a88badcdea280c
sha256
prepend 4e3e4ca04a74381180c6b4a648560e679b321b3e12d1932781b6398267151d70
sha256
prepend 61febb5707e8c9ae78c1248ca389d0dba9c00c156c2282020e27fcbae04d1810
sha256
prepend 5ab7a0c9
append 6481affe61f15ea9
verify PendingAttestation('https://bob.btc.calendar.opentimestamps.org')
-> append 3dd70ea7ab4c979a7747ab0570d2ea27
sha256
prepend b47ab96db80690d1c436022e2869404d7423f7225eb47c81436e342062c70eba
sha256
append 7c8025312aa0b452457a1a33d1e12cf0237bc34cb359140dee74f45e6ef8ead7
sha256
prepend 5ab7a0c9
append c302502f95a0f008
verify PendingAttestation('https://finney.calendar.eternitywall.com')
The OpenTimestamps proof is a chain of unary (hashing function) and binary (append, prepend) operations from the original stamped hash to the attestation. A PendingAttestation is a promise, given from the ots calendar, to put this data in future transaction.
The OpenTimestamps library timestamp can use multiple calendars in order to allow to be more reliable and a robust from side attacks.
Uploading file uploading the proof-file at opentimestamps.org and press INFO button in order to show a web visualizer of the ots proofs
Upgrade a pending proof
The ots proof can be upgraded to resolve pending attestations and in order to obtain a complete timestamp. A PendingAttestation is a promise provided by an ots calendar that only this specific calendar can resolve.
A resolved attestation is BitcoinBlockHeaderAttestation and it is verificable by block explorer.
A timestamp is completed when there are at least one bitcoin attestation. The following code allows to upgrade a timestamp:
const detachedOts = OpenTimestamps.DetachedTimestampFile.deserialize(ots)
OpenTimestamps.upgrade(detachedOts).then( (changed) =>{
if(changed){
console.log("Timestamp upgraded")
const upgradedOts = detachedOts.serializeToBytes()
const upgradedHex = bytesToHex(upgradedOts)
console.log(upgradedHex)
} else {
console.log("Timestamp not changed")
}
})
After upgrade command, the example shows the output of info command:
File sha256 hash: 16193782f1d839a08f9fc9a94cec1675f1729db1abc15cf9b57f31aa1724a0ae
Timestamp:
append c04158b183a378f3d051d55979a918d8
sha256
-> append 89c144ad44156173d93cd470569c3087
sha256
prepend d37278872acc324f499d54dd488fbe29f76d892204793701e38129e0a2f224b0
sha256
prepend 333ea54d67017894b5e581b2bd4e197d3990c031bc78331b7e5c9ee89162c8fd
sha256
append bdef644af9388e148d198dec47e62fdaf9e264baf28f9e8115f0468354b2cc44
sha256
prepend 5ab7a0c9
append 05765ac5abc32c3b
verify PendingAttestation('https://alice.btc.calendar.opentimestamps.org')
sha256
append 9392bf72d9060a7b50972524836e578e7e63dcdf14c3f5d4c1dca9d86756cb9b
sha256
append ce3d685da3581a2bb94b71cfaea03474ebe5fe40e4dca672afe7e1da742db297
sha256
prepend fce1e10cc3091a3846c93bf4aa84413fb250e5ee34b53dcad606573e3d78c4ac
sha256
append cce5fea18e0db1f32045a3eb9dfdcd4aa705fe3b180fcebf444d67c94c294c04
sha256
prepend eb3be78a0442c27bdd502552a256be442e85c47db7bf4e311cc831002b3f9b38
sha256
append 4b60e02f7497b5803e08daba5b71d48da32a173301915690e481b67f51970751
sha256
prepend b9b9f9fa9bdeb8a595bfa4eca6369506d2f1546e6b21b9c7bbd7fb2548a26ffe
sha256
append bef44e97f18402c26657532a8f73a7789105cd59f12f8d71515912470ff1fd6d
sha256
prepend 1bc0e9e84a56d090d0b3c3eb4f82e2d540f0ed7a814c3c8c408d2f578dfea53d
sha256
append 4e315507d6bfd306166e1020bd051d71e783ea1082d22013304626f7c5a279e6
sha256
append e5e9e4a6fe92bb4477cea41e2c15c2c16510bef0b45b269a9f0baba752ea2c8b
sha256
prepend 76242fc7615358d5cf2faa3ce7c0fea8eda591c128a7ab7f881bfc9da5dd96e2
sha256
append 59942d9922a624ddd4b4ce58de992436565db8cf682dbe98cfb1e71bd6a6a049
sha256
prepend 01000000012eac8b315182773e76d57edd23b0297f60c2b5cce26e8b1958609bf53f17c998000000001716001405b45b2e5fb44a6f875d69cb4df5d414f7ba1c34fdffffff02588665000000000017a9146f626afde13c6395faad1615fe281d5c0be123c0870000000000000000226a20
append 22dc0700
# transaction id fd02844474819a15ae726e2f7e75d0eeb7e5de497c918ee69758130e41e30cbc
...
verify BitcoinBlockHeaderAttestation(515107)
# Bitcoin block merkle root 7d7cd153b837a18ba32b21af103af1691b1ba3d4248e7fc9c290211e15de37d5
-> append 26ef6425656e1095c5a88badcdea280c
sha256
prepend 4e3e4ca04a74381180c6b4a648560e679b321b3e12d1932781b6398267151d70
sha256
prepend 61febb5707e8c9ae78c1248ca389d0dba9c00c156c2282020e27fcbae04d1810
sha256
prepend 5ab7a0c9
append 6481affe61f15ea9
verify PendingAttestation('https://bob.btc.calendar.opentimestamps.org')
...
# transaction id df7b8ba0739571e6508f812c82de25259059bd5129a4f96816567480d3718692
...
verify BitcoinBlockHeaderAttestation(515104)
# Bitcoin block merkle root 8331bed61eb2858361b16ac337da5fdacf9b3ee41f6c8f1e204a983b9fccdb36
-> append 3dd70ea7ab4c979a7747ab0570d2ea27
sha256
prepend b47ab96db80690d1c436022e2869404d7423f7225eb47c81436e342062c70eba
sha256
append 7c8025312aa0b452457a1a33d1e12cf0237bc34cb359140dee74f45e6ef8ead7
sha256
prepend 5ab7a0c9
append c302502f95a0f008
verify PendingAttestation('https://finney.calendar.eternitywall.com')
...
# transaction id 355d3a6da112e10a589b84eb3d45682c79b1a85dbd1a3720ccf7c7bf40b02969
...
verify BitcoinBlockHeaderAttestation(515107)
# Bitcoin block merkle root 7d7cd153b837a18ba32b21af103af1691b1ba3d4248e7fc9c290211e15de37d5
Now the timestamp is completed and each incomplete PendingAttestation has become a BitcoinBlockHeaderAttestation with the corresponding block height. The bitcoin block contains the timestamp, so the date, of the stamped operation.
Follow the crypto-operations path from hash to attestation, to get the merkle root of the bitcoin block.
To verify manually the ots proof: open a block-explorer and check if the block height and merkle root inside the attestation match.
Verify the ots proof on the blockchain
OpenTimestamps library provides the verify command to check the integrity of a proof and verify all the completed attestations in order to get the date of the proof.
const hashData = "16193782f1d839a08f9fc9a94cec1675f1729db1abc15cf9b57f31aa1724a0ae"
const op = new OpenTimestamps.Ops.OpSHA256()
const detached = OpenTime
stamps.DetachedTimestampFile.fromHash(op, hashData)
const detachedOts = OpenTimestamps.DetachedTimestampFile.deserialize(ots)
OpenTimestamps.verify(detachedOts, detached).then( (results)=>{
if(Object.keys(results).length === 0){
console.log("Pending attestation");
}else{
Object.keys(results).forEach(key => {
console.log ( key+" attests data existed as of " + (new Date(results[key] * 1000)) );
});
}
}).catch( err => {
console.log("Bad attestation" + err);
});
The result is the unix timestamp of the first completed attestation, with lower block-height, in the example is {bitcoin: 1521990170}. The previous code formats the unix timestamp and show the following message: Bitcoin attests data existed as of Sun Mar 25 2018 17:02:50 GMT+0200
OpenTimestamps proof supports multiple chains, a multi-chain proof is verified in both the chains and providing different timestamps.